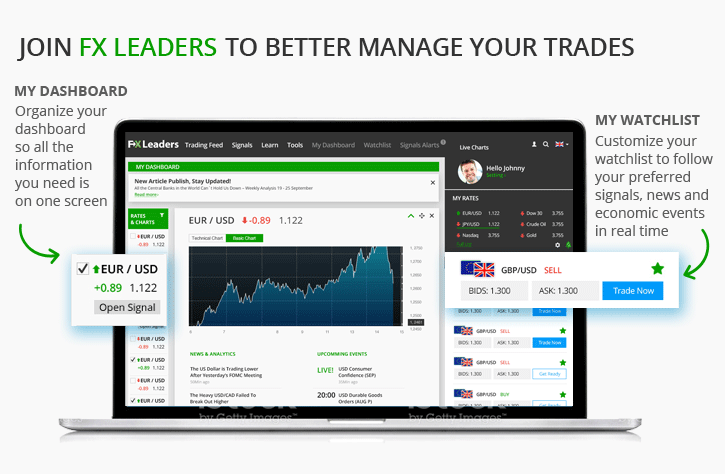
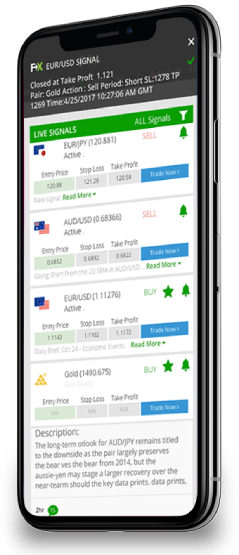
What is DeFi (Decentralized Finance)?
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is an emerging global financial system based on blockchain technology and its secure distributed ledgers, which cuts out the intermediaries, such as banks, brokerages and financial institutions. This new technology makes the connection between the parties, giving them control over funds and exposure to financial products and services all over the globe. The DeFi sector is part of the crypto industry, where participants can borrow funds without paying fees to the intermediary, and they can also lend funds, in order to earn interest in liquidity pools, or they can speculate on cryptocurrencies, insure against risks etc. The architecture of DeFi is layered in 3 different blockchain levels, which offers opportunities to earn high interest across different networks. Ethereum, which was the network that introduced smart contracts, is the main DeFi network. In recent years, leverage has also come to DeFi, offering even higher returns, albeit with an increased risk.
What is DeFi Lending
DeFi loans are one of the fastest growing sectors in the crypto industry, by total value locked (TVL). Users can borrow funds without the middleman, directly through a peer-to-peer (P2P) decentralized lending platform, by providing a crypto collateral. This enables lenders to earn interest or fees on their funds.
What is DeFi Yield Farming?
Yield farming is an investment technology that enables holders of crypto tokens to maximize returns by staking, in return for interest. Yield farmers place their cryptos into a liquidity pool, which is a place where everyone can borrow tokens, where they are locked for a period of time, earning fixed interest from liquidity providers (LP).
What is an AMM (Automated Market Maker)?
Automated market makers facilitate the exchange between two people, without a third party who enables the transaction. AMMs are liquidity providers in decentralized exchanges, which provide cryptocurrency crosses in the form of liquidity pools, via smart contracts. So trades are peer-to-contract, instead of being P2P, and therefore part of the decentralized exchanges.
What is a DEX?
Decentralized exchanges are a cryptocurrency marketplace which can be peer-to-peer or peer-to-contact. DEXs are built on blockchains via smart contracts, and they can bring a number of crypto-related services directly to your wallet, allowing users to hold their funds at all times. They use automated algorithms, which bypass traditional centralized exchange institutions.
What are Cross Chain Bridges?
Blockchain bridges facilitate the connection between vastly different networks. They enable blockchains to communicate with each other by transferring information and assets, such as cryptocurrencies, smart contracts etc. Bridges also connect the three different layers of blockchains, enabling dApps built on these networks to access the benefits of different blockchains.
What are Crypto Options?
A crypto option is a derivative contract that offers the bearer the right to execute a trade on or before an expiration date, but they are not obliged to do so. Crypto options often offer the buyer a low-risk solution for trading cryptocurrencies. Call options give the holder the right to buy a crypto asset; Put options give the holder the right to sell a crypto asset.
What are Tokenized Bonds?
Tokenized bonds are a new financial instrument in the crypto industry. They are also referred to as blockchain bonds or smart bonds, and in essence, they are automated contracts issued on a blockchain. They are representations of ownership via crypto tokens, which can be transferred, stored or registered in a blockchain, where terms are automated.
What are Crypto Derivatives?
A crypto derivative is a contract between two people to trade the difference in the price of a crypto asset at a certain time. The seller and the buyer of the derivative do not trade the crypto token, since they don’t own it, but they speculate on the future price at the time of expiration. Crypto derivatives come in the form of futures, forwards, options and swaps.
What are On-chain synthetic Assets?
Crypto synths are a combination of crypto assets and traditional derivative assets. They are tokenized representations of derivative stocks, or derivatives that a trader does not own, but wants to buy or sell, mimicking the value of another asset. Crypto synths offer exposure to a wide range of financial assets around the world, from within the crypto ecosystem.
What are Cryptocurrency Perpetuals?
A crypto perpetual contract is a type of derivative trading product known as perpetual swap. It works like a futures derivative, where holders don’t own the asset, but there is no expiration date. Perpetuals are agreements to non-optionally buy or sell a crypto token, but with an unspecified time of execution.
What is Cryptocurrency Staking?
Crypto staking is a way for token holders to earn passive income on Proof-of-Stake blockchains, which use this method to help verify transactions on the network. By staking, investors lock their crypto tokens in liquidity pools, which act as validators to confirm blocks of transactions, thereby earning freshly minted coins as rewards for their staked assets.
What is Cryptocurrency Total Locked Value (TVL)?
The Total Value Locked is the overall value of crypto assets that are presently being staked in a DeFi protocol. The crypto networks use the TVL tokens to build these blockchain protocols from the bottom up, and offer interest, coin rewards, fixed income, etc. in return. It has emerged as a key metric for the health of the DeFi sector, with Ethereum deposits accounting for over half of the total TVL in the crypto market.
What is Impermanent loss?
Investors face impermanent loss when the temporary decline in the value of crypto assets exceeds the fees that liquidity providers receive, such as interest or newly minted coins. This is the risk that comes from market volatility, and that liquidity providers face when they stake their crypto assets in liquidity pools.
What is a Rebase Token?
Such coins are also considered price-elastic tokens, as they adjust in response to the supply and demand. Rebase refers to adjusting the circulating capacity by burning old coins or adding new coins to the total supply, in order to keep the price within a specific range. The circulating supply is adjusted automatically or periodically, according to price fluctuations.
What is a Decentralized Autonomous Organization?
This refers to crypto decentralized autonomous organizations built on blockchains, which is a public ledger system with decisions made from the bottom up. A DAO is a community entity, governed by its individual members, who can coordinate to pool funds or create tokens.
What is a Decentralized Application
A dApp is a decentralized digital software application that can operate autonomously. dApps are built on decentralized blockchains, where the backend code runs on a peer-to-peer network. It consists of a smart contract backend and a user interface that can be developed for purposes such as investing, gaming social media etc.
What are Gas Fees?
Gas fees refer to the cost of doing a transaction on the Ethereum blockchain. Users pay miners on the blockchain a fee to have their transaction included in the block, and the fees adjust according to the supply and demand. The higher the demand for transactions, the more miners will request for transactions.
What are Liquidity Pools?
LPs are smart contracts with a certain amount of crypto assets locked in, which are kept to provide liquidity. Liquidity pools are crowd sourced and they facilitate trading on decentralized exchanges. They are based on self-executing programs that enable the exchange of digital assets automatically through them.
What are Cryptocurrency Tokenomics?
The total economics that drive a crypto asset are referred to as tokenomics. It is the most important factor when deciding whether a crypto token has growth potential. Tokenomics shows the real value of a crypto asset, as it takes the supply and demand, functionality, allocation policy, objective etc. into account.
What are Pegged Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are a class of crypto tokens that are pegged to more stable assets, such as fiat currencies, currency baskets, etc. Their goal is to provide price stability and make the connection between the financial market and the crypto market. Stablecoins are backed by real-life assets, in order to preserve their value. The most popular one is Tether USDT.
Cryptocurrency Wallets
Moving money is becoming cheaper and easier, especially in this era of cryptographic digital currencies, plainly called cryptocurrencies... Full Article
Cryptocurrency Exchange
The cryptocurrency market is booming and so are cryptocurrency exchanges. Most exchanges perform the important task of converting fiat Full Article
Best Cryptocurrencies to Invest in 2022
Cryptocurrencies began with Bitcoin a decade ago, but in recent years this market has taken everything by storm. Who would have imagined 5 . Full Article
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The moving average convergence divergence (MACD, pronounced “Mac-D”) is a momentum-based indicator that illustrates the correlation betw... Full Article
Cryptocurrency Trading: Price Action
Cryptocurrencies - who would have thought that this strange asset class would attract so much attention and such a massive amount of inve... Full Article
Cryptocurrency Trading: Buy-and-Hold
No other asset class has seen the magnificent gains which were recently seen in cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, the most prominent cryptocurr... Full Article