Crypto Guide: What is Bitcoin Currency?
What is Bitcoin? Many people who hear of Bitcoin for the first time find it hard to comprehend what it actually is and how it functions as a currency. After all, bitcoin, commonly denoted as BTC or XBT, doesn’t function like a traditional fiat currency or investment vehicle.
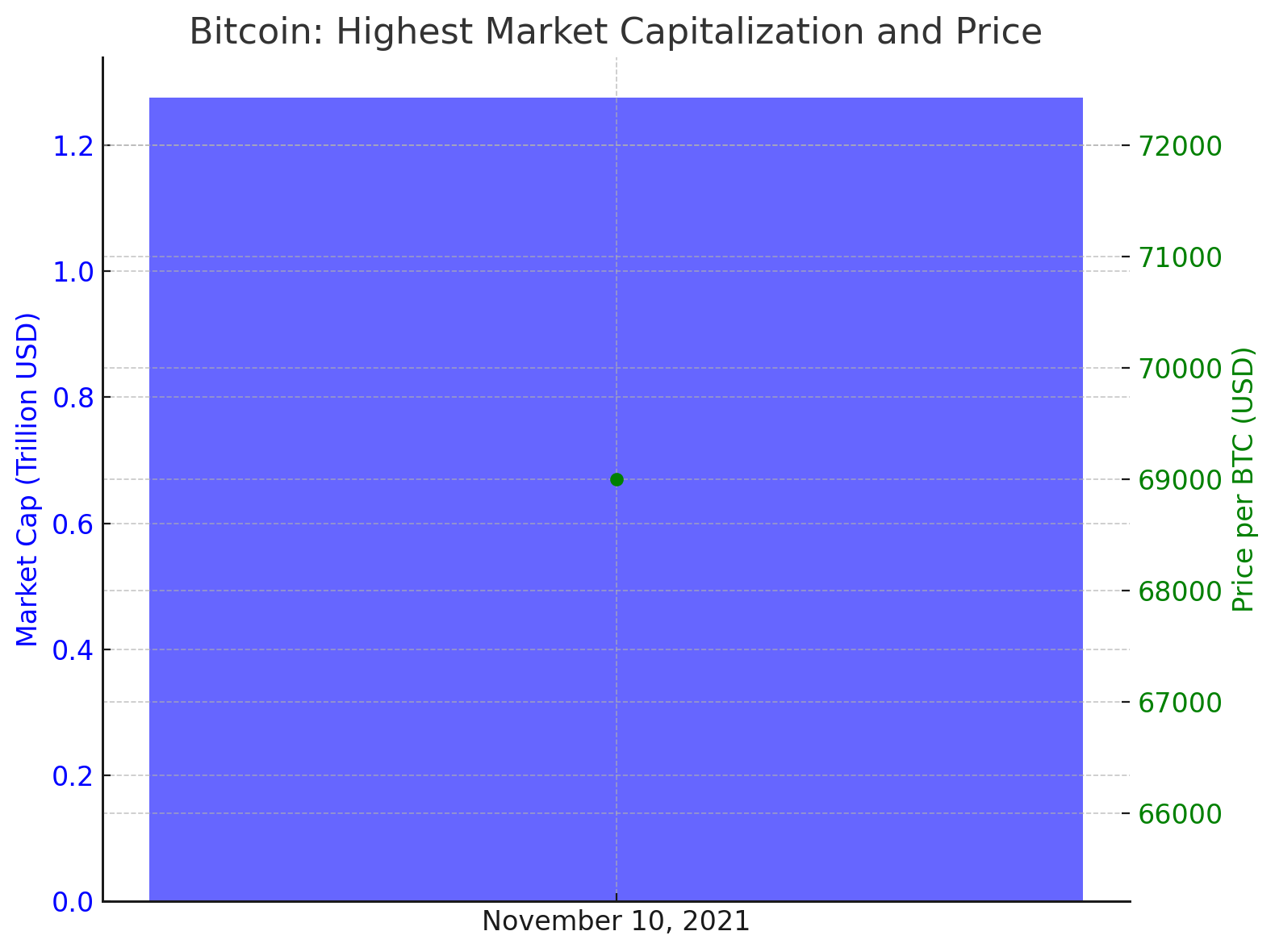
As of July 2024, the highest market capitalization and price for Bitcoin were recorded on November 10, 2021, when its market cap reached approximately $1.276 trillion, and the price peaked at around $69,000 per BTC.
However, bitcoin’s price is known for its volatility, with significant fluctuations that can impact both buyers and merchants, making it a less ideal payment option for some.
Its daily trading volume of approximately $22 billion underscores its importance as not just a medium of exchange, but also a symbol of financial innovation, autonomy, and the potential for substantial investment returns.
Curious why Bitcoin has captured the imagination of millions? Let’s dive into what makes this digital currency so unique.
Bitcoin images like this one are merely symbolic of the real bitcoin currency, which is completely digital and intangible.
What is Bitcoin / Bitcoin Explained
Bitcoin is a digital or virtual currency that is created (mined), stored, traded, and transferred electronically. Bitcoin (BTC or XBT) is not regulated by any central bank or central authority and can easily be transferred between individuals or businesses around the world without any oversight.
To understand how Bitcoin works, it is essential to know that it relies on blockchain technology, transaction verification, and mining to facilitate decentralized financial transactions.
The SHA-256 decreasing supply algorithm limits the pace at which Bitcoin can be mined and its maximum supply. This means that mining Bitcoin becomes progressively harder, a process known as ‘halving’.
The SHA-256 algorithm also limits the amount of bitcoin that can be mined to 21 million units, with the last bitcoin expected to be mined in the year 2140. This mechanism is beneficial for the price of Bitcoin because it limits supply while demand, in theory, increases exponentially.
Bitcoin has become a powerful financial instrument that is traded and speculated on more and more every day.
Bitcoin’s Unique Features

Bitcoin stands out in the world of digital finance due to its unique characteristics:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin operates without a central authority, making it immune to government interference.
- Transparency: All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain, ensuring complete transparency.
- Security: Bitcoin transactions are secured by cryptographic techniques, making them highly secure.
- Proof of Work: The proof-of-work consensus mechanism validates Bitcoin transactions and secures the network. Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to authenticate transactions, which rewards them and prevents fraud through decentralized verification.
- Limited Supply: With a cap of 21 million bitcoins, scarcity is built into the system, often compared to precious metals like gold.
Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions are peer-to-peer, meaning they can be sent directly from one party to another without needing an intermediary like a bank. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how a Bitcoin transaction works:
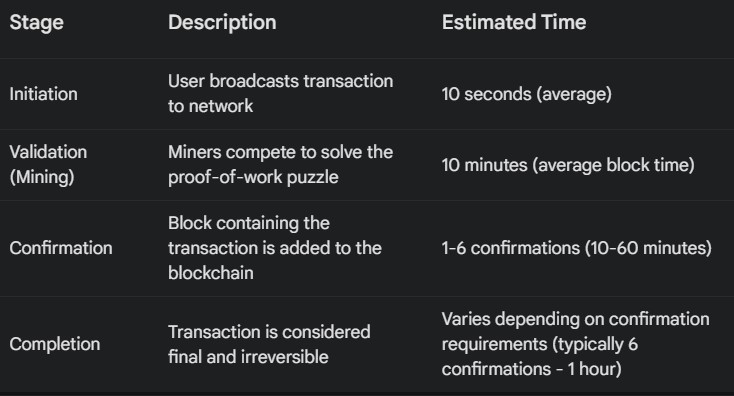
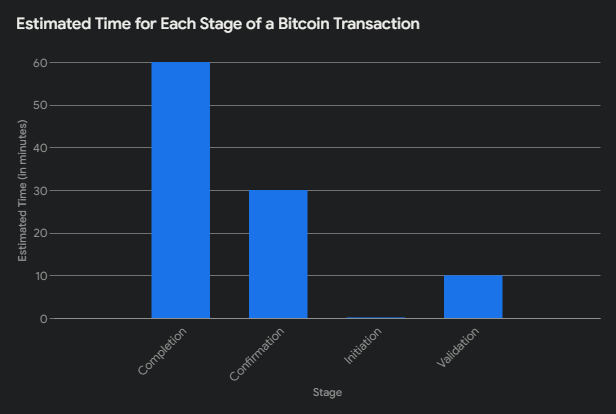
- Initiation: A user initiates a transaction from their Bitcoin wallet.
- Validation: The transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network, where nodes (computers) validate the transaction using the blockchain. Miners play a crucial role in validating transactions and verify transactions to ensure they are consistent with historical records, preventing issues like double spending.
- Confirmation: Once validated, the transaction is added to a block. Miners compete to solve the block’s cryptographic puzzle.
- Completion: After the block is mined, the transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain.
*Learn how to trade bitcoin here.
Bitcoin History
Meet the Mastermind: Who Really Invented Bitcoin?
An anonymous mastermind with the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto invented a powerful peer-to-peer money transfer system in 2009, based on decentralized blockchain-ledger technology.
A blockchain ledger is a digital, decentralized ledger that is distributed between numerous nodes (computers).
The record of a particular transaction cannot be altered without changing the subsequent blocks, which are linked to the block that contains the record of that particular transaction.

Nakamoto created a decentralized currency like the world had never seen before, inventing a new way to send currency between friends, relatives, or even unknown entities who can remain anonymous.
The first genesis block was mined in January 2009, and the world has never been the same since.
The Purpose Behind Bitcoin: Why It Was Invented
Bitcoin was invented to provide a means of transferring money electronically without being governed by a central authority. The purpose was to enable quick and cheap peer-to-peer money transfers with a reliable decentralized system that effectively prevents double-spending.
Double-spending simply means spending the same bitcoin (or amount of bitcoin) twice. This can be a problem with digital cash transactions because each portion of digital currency has a digital file that can be duplicated and used to spend the same ‘coin’ more than once if proper precautionary measures are not taken.
With traditional paper money, this is not a problem. For example, if a child hands a $10 bill for some sweets at a candy shop, they cannot spend the same $10 bill again because, after the transaction is confirmed, the bill is no longer in their possession.
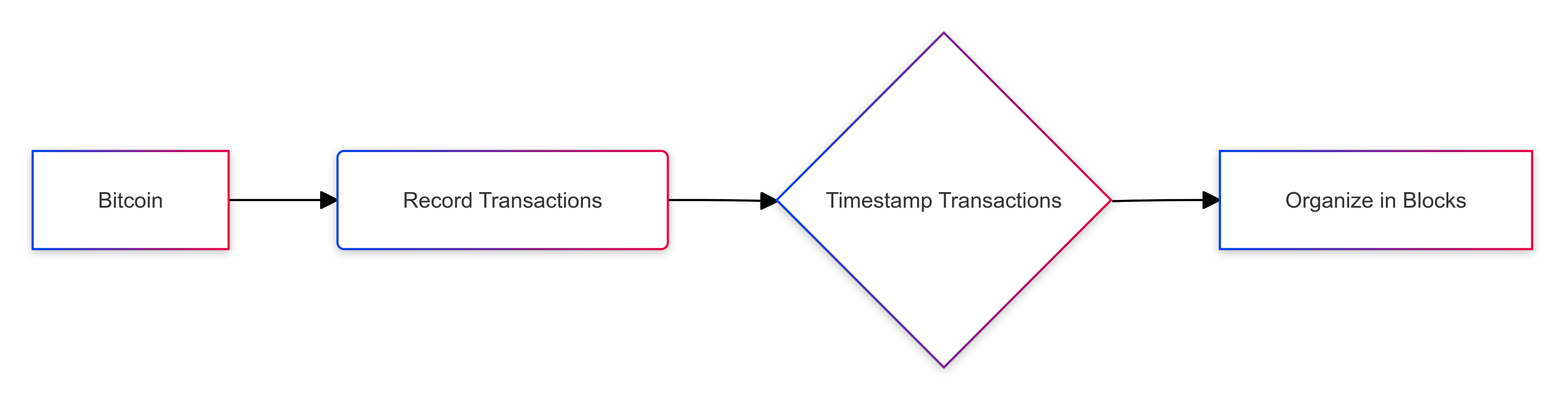
Bitcoin uses an effective confirmation mechanism that:
- Records every transaction performed on the blockchain,
- Gives each transaction a timestamp and unique identifier, and
- Organizes transactions chronologically in ‘blocks’.
A log of digital signatures accompanies every bitcoin transaction, tracking the ownership path by which the currency has been transferred. If someone tries to simultaneously spend the same bitcoin twice, only one transaction will be confirmed, with the other one being rejected. The only way to double-spend is by ‘forking’ bitcoin, which creates an entirely new, essentially worthless cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin Mechanics
Blockchain Technology / Decentralized Blockchain Ledger
The entire Bitcoin network is managed by a distributed ledger that uses blockchain technology to keep track of transaction paths and prevent double-spending.
This ledger is maintained by thousands of nodes (computers) that process transactions on the network. These nodes receive rewards (bitcoins and transaction fees) for their processing efforts, which involve organizing ledger information into new blocks and finding a valid hash. This process is known as bitcoin mining.
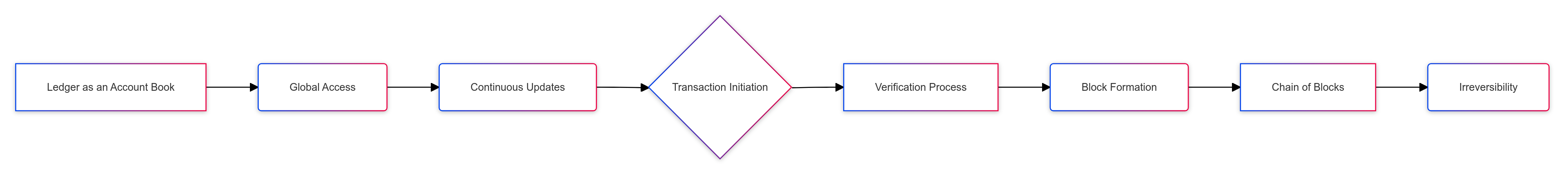
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how the Bitcoin blockchain ledger works:
- Ledger as an Account Book: The ledger functions like a register or log, similar to what an accountant would use.
- Global Access: The entire bitcoin ledger is simultaneously accessible to all nodes worldwide.
- Continuous Updates: The ledger is continuously updated, ensuring every computer has the most current version.
- Transaction Initiation: When a transaction is initiated on the Bitcoin network, it is distributed to all network computers.
- Verification Process: Nodes verify the transaction with other computers to ensure accuracy.
- Block Formation: Verified transactions are packed into a block of data comprising multiple Bitcoin transactions.
- Chain of Blocks: Completed blocks are attached in chronological order to the existing blockchain, like links in a chain.
- Irreversibility: Once transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain, they cannot be reversed. Blocks cannot be removed or replaced, making them final.
After a block is added to the blockchain, mining begins on the next block, and the process repeats.
Limited Bitcoin Supply: The 21 Million Cap
The algorithm governing Bitcoin mining imposes a limit on the rate at which bitcoins can be mined and caps the total supply at 21 million bitcoins. It is estimated that the last bitcoin will be mined in 2140. This limited supply supports Bitcoin’s price, contrasting with the often-increasing supply of fiat currencies.
For example, unlike fiat currencies that central banks can print more of, Bitcoin’s finite supply is similar to precious metals like gold, which are also limited in quantity, contributing to their value.
Bitcoin Market Capitalization and Trading Volume
Bitcoin’s market capitalization is highly dynamic and experiences frequent fluctuations. As of July 2024, its market cap stands at approximately $1.3 trillion, a testament to its continued dominance in the cryptocurrency market.
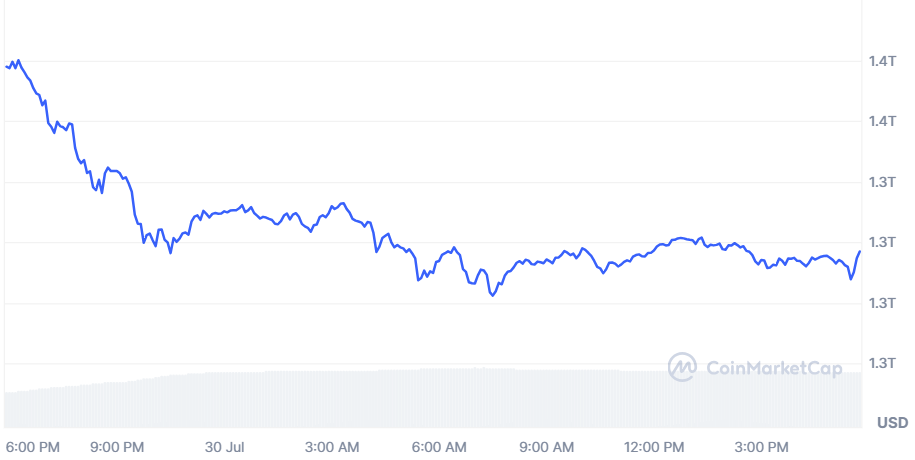
The daily trading volume of Bitcoin is also substantial, often exceeding $30 billion. While impressive for a cryptocurrency, this figure is still dwarfed by the trading volumes of major currency pairs like EUR/USD, which regularly surpass $1 trillion per day.
This comparison highlights the relative nascency of the cryptocurrency market compared to established foreign exchange markets.
Bitcoin Transfers/Transactions
Bitcoin, in theory, can be transferred from one Bitcoin wallet to another with minimal transaction fees. However, these fees depend on the activity on the network.
For example, during a strong bull market, the block size increases, allowing users to pay higher fees to expedite their transactions through the network.
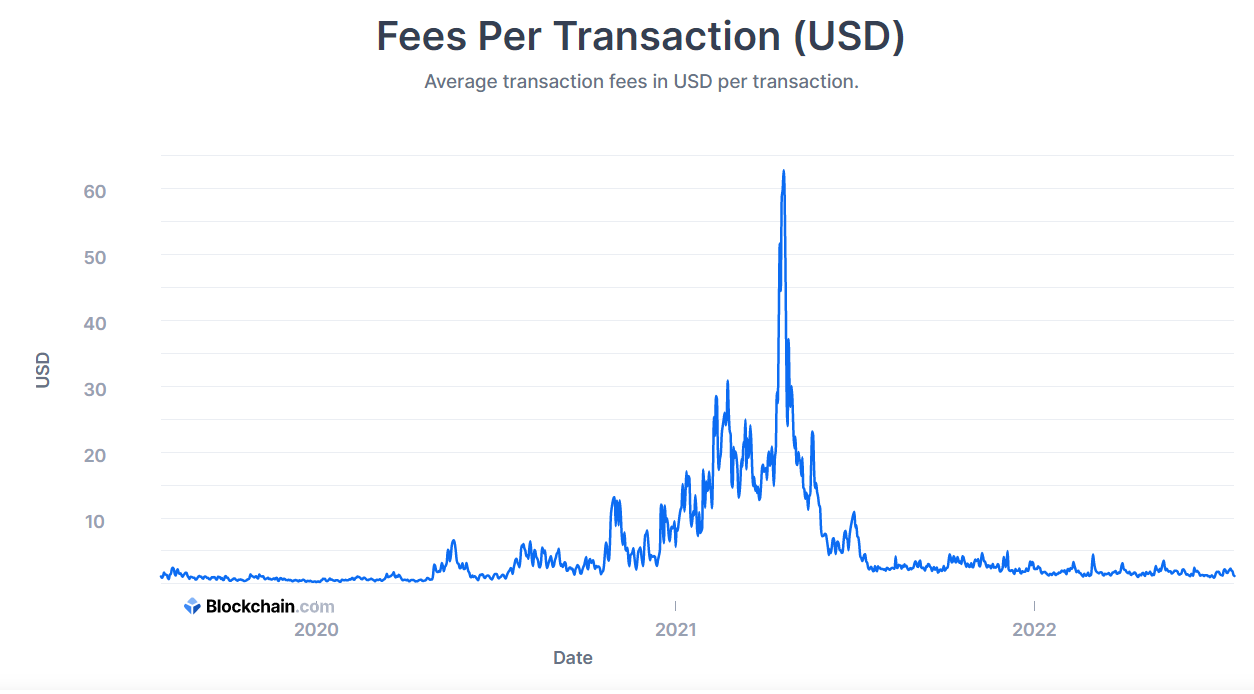
During quieter times, fees are generally around a few dollars. At their peak in mid-2021, fees reached an extortionate $62.
This fee structure depends more on the transaction’s size in bytes and urgency than on the amount being sent; transactions with higher fees are prioritized.
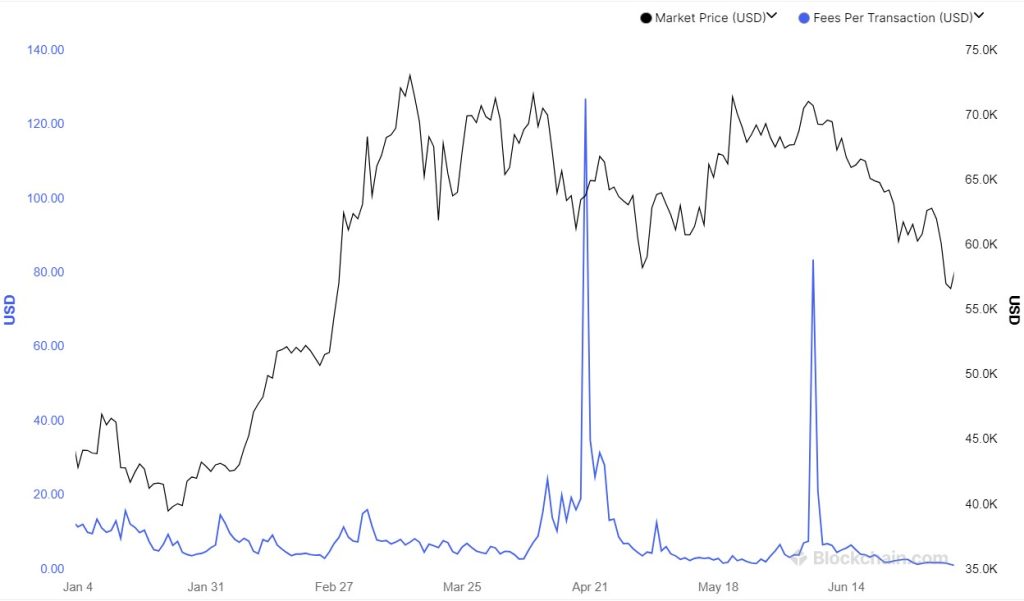
Further spikes in transaction fees were seen around April 20, 2024, when fees surged again to around $127, reflecting another period of high network activity and increased demand for quick transaction processing.
During these peaks, the fees depend more on the transaction’s size in bytes and its urgency rather than the amount being sent, with higher fees ensuring faster transaction confirmation.
Many merchants and businesses, including both large companies and local retailers, now accept Bitcoin as a payment method.
Both brick-and-mortar stores and online businesses can choose to accept Bitcoin, often advertising this with signs. To conduct transactions, it is necessary to have a cryptocurrency wallet.
How Do Bitcoin Transactions Occur?
- Initiation: The transaction is initiated from a Bitcoin wallet.
- Validation:
- Every node with a copy of the blockchain validates the transaction, checking that the sender’s wallet has enough bitcoins.
- Memory Pool:
- After validation, the transaction enters the Memory Pool, a waiting area where transactions wait for miners to add them to a block.
- Confirmation:
- Once added to a successfully mined block, the transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain.
For example, if Alice wants to send 0.5 BTC to Bob, she initiates the transaction from her wallet. The network nodes validate that Alice has enough bitcoins. The transaction then enters the Memory Pool.
Once miners include it in a block and the block is mined, Bob will see the 0.5 BTC in his wallet, confirming the transaction.
Using this structure ensures that transactions are secure, transparent, and efficiently processed within the Bitcoin network, maintaining the integrity and trust in the decentralized system.
How to Buy Bitcoin with Fiat Currencies (Dollars, Pounds, Euros, etc.)
To pay for something with Bitcoin or to send Bitcoin to someone, you first need to have some Bitcoin. To receive a Bitcoin payment/transfer, you only need to set up a Bitcoin wallet and provide the sender with your wallet’s address.
Parties who need to fund their Bitcoin wallets can convert fiat currencies to Bitcoin in several ways. One common method is to create an account on a cryptocurrency exchange and fund it using a bank account.
This allows users to purchase Bitcoin with fiat currency, such as U.S. dollars, by transferring money from their bank account to the exchange.
1. Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Open an account with a reliable cryptocurrency exchange, like Binance, Kraken, or Coinbase. After depositing money via your credit card, debit card, or a wire transfer (electronic funds transfer), you can trade it for Bitcoin on the exchange.

Once you have Bitcoin, you can send it to anyone who provides you with a valid Bitcoin address. You can also receive Bitcoin payments into the account you have with the cryptocurrency exchange with your unique wallet address.
Some cryptocurrency exchanges offer the option of converting bitcoin and certain fiat currencies to other cryptocurrencies besides bitcoin. For example, you can trade bitcoin for Ethereum (ETH) using the BTC/ETH pair.
2. Bitcoin Marketplaces
Bitcoin can be acquired with cash, credit cards, wire transfers, etc., by locating individuals in Bitcoin marketplaces who want to sell Bitcoin. These marketplaces, like LocalBitcoins or Paxful, facilitate direct trade between individuals.
Often, there will be dedicated sellers on these platforms you can choose from. Sometimes, the transaction can even be conducted in person if you prefer.
Bitcoin can be bought in many different ways with fiat currencies in Bitcoin marketplaces, including cash and bank wire transactions.

3. Bitcoin ATMs
Bitcoin ATMs are popping up worldwide. To buy bitcoin with cash at a bitcoin ATM, follow these steps:
- Select ‘buy’ when prompted by the ATM.
- Choose the amount of bitcoin you want to purchase.
- Insert cash into the ATM.
- Scan the QR code of your Bitcoin wallet address to receive the Bitcoin.
- Wait for the transaction to be confirmed. This wait can vary depending on the network activity.
Imagine you have $100 in cash and want to buy Bitcoin. You find a Bitcoin ATM in your city, follow the steps above, and within minutes, you receive the equivalent amount of Bitcoin in your digital wallet.
Selling Bitcoin at a Bitcoin ATM
To sell Bitcoin and withdraw cash at a Bitcoin ATM:
- Select ‘sell’ when prompted by the ATM.
- Choose the amount you want to sell in Bitcoin and request to withdraw cash.
- Scan the QR code presented to you, either on screen or on a printed receipt.
- Wait for the transaction to be confirmed. This wait can vary depending on a few factors, like the amount sold. Some machines will send you a text message telling you your cash is ready; others require you to come back and scan a QR code on your receipt.
- Redeem and withdraw your cash.
Bitcoin ATMs provide a convenient way for people to buy and sell Bitcoin with cash.
Understanding Bitcoin Wallets and Exchanges
One of the main differences between Bitcoin wallets and exchanges is that with an exchange, fiat currencies can be converted to Bitcoin and vice versa. These exchanges generally offer a selection of other cryptocurrencies to buy and sell, ranging from a handful to hundreds.
Exchanges usually provide you with a unique address to send and receive BTC, enabling you to use it like a regular Bitcoin wallet. However, be wary of keeping funds on exchanges, as hacks do occur, and you might not get your money back.

For instance, Imagine you have $500 and want to buy Bitcoin. You can:
- Use an Exchange: Open an account on a platform like Binance or Coinbase, deposit your $500, and trade it for Bitcoin. The exchange gives you a unique Bitcoin address, and you can send and receive Bitcoin using this address.
- Use a Bitcoin Wallet: Transfer your Bitcoin from the exchange to a Bitcoin wallet for added security. Wallets like Ledger or Trezor store your Bitcoin offline, reducing the risk of hacking.
Using an exchange allows you to convert fiat currencies to bitcoin easily, but transferring your funds to a secure wallet is recommended to protect your assets.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets
1. Desktop Wallets
- Bitcoin Clients
Bitcoin clients function in the same way as the original Bitcoin wallet, BitcoinQt, which is now called Bitcoin Core. Bitcoin Core is a ‘full client’ or a full node client that requires strong computing power. It’s the most reliable wallet but is slow and not ideal for the casual user.
When Bitcoin Core is downloaded, the whole blockchain is downloaded to your computer, which can be dozens of gigabytes. Lightweight clients like Electrum are easier to use and can even be operated from a smartphone.
- Other Desktop Wallets
Desktop wallets other than Bitcoin Core include Armory, Electrum, Bither, and Wasabi. For a full list, check out bitcoin.org’s directory.
2. Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets, like Edge, Mycelium, or Unstoppable, are bitcoin wallets that are installed on your smartphone, and these are often lightweight and agile. A great feature of these wallets is that they allow you to quickly scan QR codes for easy transactions.
3. Physical Wallets
Paper wallets are a reliable form of cold storage where bitcoin can be stored safely. Paper wallets basically have the public address of your Bitcoin wallet (which you need in order to receive Bitcoin transfers) and the private key that can recover your wallet.
In order to spend these bitcoins, one must ‘sweep’ the private key into an active wallet, which loses the benefits of cold storage. Still, paper wallets are a very secure way to hold Bitcoin.
4. Online Wallets
Online wallets offer perhaps the easiest way to create a wallet, with many giving you an address within minutes. No need to download the blockchain; just log in and start sending and receiving. One of the most popular options is Blockchain.com
With this option, your private keys are stored on the website’s server, which means recovery of your wallet, should you lose access, is easy if you’ve stored the private key yourself. However, you may lose control over your private keys if the online service provider doesn’t take the necessary precautions to secure them.
5. Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets like a Ledger or Trezor can facilitate secure Bitcoin payments and store private keys electronically without ever actually exposing them. The main benefit of using a hardware wallet is that secure Bitcoin transactions can be made on a computer that might not be secure.
Another advantage is that parties with large amounts of Bitcoin can safely store Bitcoin and execute Bitcoin transactions without having to rely on third parties for security. Hardware wallets are the best option for anyone seriously considering holding and storing Bitcoin.
The Risks of Bitcoin: Loss and Theft in the Digital Age
While Bitcoin offers revolutionary financial possibilities, it’s not immune to loss or theft.
- The history of cryptocurrency is riddled with high-profile security breaches, with the Mt. Gox incident in 2014 being a stark reminder of the risks. In this infamous hack, approximately 850,000 bitcoins (worth billions of dollars today) were stolen from the exchange’s customers.
- In more recent times, the 2023 hack of Atomic Wallet resulted in losses exceeding $100 million. These events underscore the importance of robust security measures when dealing with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Beyond exchange hacks, individual users also face the risk of losing their Bitcoin due to misplaced private keys or compromised wallets. A private key is like the password to your Bitcoin holdings – lose it, and your Bitcoin is effectively gone forever. Stories abound of individuals losing access to substantial Bitcoin fortunes due to forgotten passwords or lost hardware wallets.
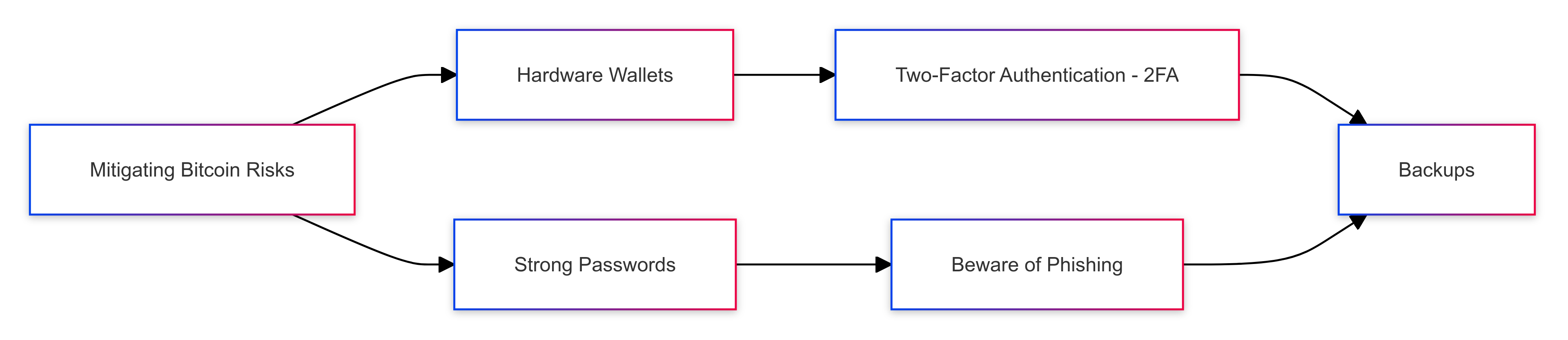
To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to adhere to security best practices:
- Hardware Wallets: Store your Bitcoin on a hardware wallet, a physical device that keeps your private keys offline and away from potential hackers.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for your online accounts and wallets.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Beware of Phishing: Be vigilant about phishing scams that attempt to trick you into revealing your private keys or login credentials.
- Backups: Regularly back up your wallet data and store it in secure, offline locations.
Remember, with great potential comes great responsibility in the world of cryptocurrency.
Why is Bitcoin so Popular?
Bitcoin’s popularity remains steadfast in 2024, driven by a unique blend of characteristics that set it apart from traditional financial systems.
- Cheap and fast transactions – Bitcoin transactions are generally cheap to carry out. To move $1,000,000 worth of bitcoin from South Africa to Hawaii (Hawaii is basically antipodal to South Africa) can be done for less than $10… in less than an hour. Now that’s awesome!
- Anonymity – There are no names attached to wallets. While they can be traced when a wallet is linked to a verified person’s wallet, in theory, one could perform a transaction completely anonymously.
- Low risk of fraud – As mentioned, the only way to fraudulently transact bitcoin is by stealing it. Other than that, double-spending and other fraud is virtually impossible.
- Lack of centralization—Banks are no longer needed as intermediaries to transact globally. There are no taxes or dependence on a larger authority in the Bitcoin world.
- Extreme price volatility and price escalation – Large volatility provides an opportunity for excellent speculative and investment growth.
- Growing adoption – as institutions, central banks, and even entire governments adopt bitcoin, the price is likely to grow. This attracts many sold on the prospect of high returns for years to come.
Fast Bitcoin transactions have drawn many users to this amazing cryptocurrency.

Could Bitcoin ‘Crash and Burn’?
It’s definitely possible, but due to the overall increasing confidence in Bitcoin and its immense popularity, a major crash is not likely to happen very soon. Famous skeptics, like Warren Buffett, predict Bitcoin will eventually return to $0; some see the value but feel physical assets like gold will always trump digital assets and are wary of the prospect of long-term growth.
Generally speaking, a catastrophic event would need to play out in the Bitcoin world for the price to sink to $0. There are currently around 250,000 Bitcoin transactions every day; for Bitcoin to fall that far, that number would need to decrease significantly.
Factors That Could Lead to a Crash:
- Regulatory Crackdowns: Stricter regulations or outright bans by major governments could severely impact Bitcoin’s value.
- Technological Failures: A critical flaw in Bitcoin’s technology or a successful hack could undermine trust in the cryptocurrency.
- Market Manipulation: Large-scale market manipulation by whales (large Bitcoin holders) could cause drastic price drops.
- Loss of Interest: If investors and users lose interest in Bitcoin in favour of newer, more advanced cryptocurrencies, its value could plummet.
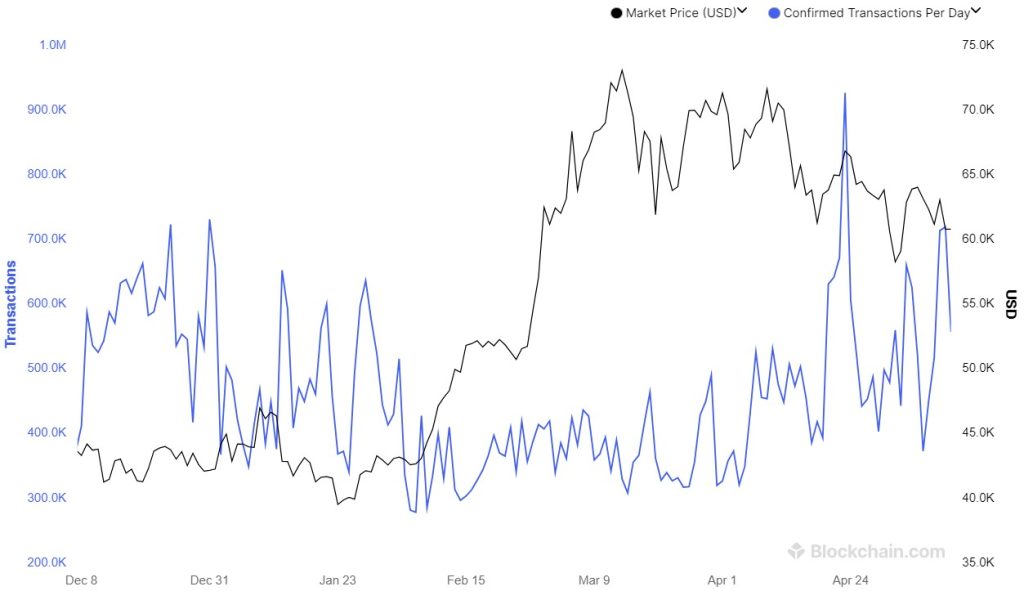
Bitcoin Market Dynamics
From December 2023 to May 2024, Bitcoin’s market price fluctuated between $40K and $75K USD. Daily confirmed transactions ranged from 200K to 1M, peaking at around $70K in April 2024, highlighting significant market activity.
Is Bitcoin a Safe-Haven Asset?
Many people consider Bitcoin a good store of value and a hedge against central bank failure.
However, given its volatility and relatively thin liquidity compared to major currency pairs, most financial professionals don’t see it as a reliable safe-haven asset. Gold and the Japanese Yen are examples of widely accepted safe-haven assets.
A major drawback of Bitcoin is that it has little intrinsic value besides being a store of value. This is why some call it digital gold, despite gold having other uses in manufacturing. Bitcoin’s status as a safe-haven might improve if its volatility decreases and its liquidity increases.
Alternatively, Bitcoin might fade away in the future; it’s impossible to know for sure.
One argument for Bitcoin’s potential as a safe-haven asset is its recent adoption as legal tender in El Salvador and the Central African Republic (CAR).
According to news, the government of El Salvador made Bitcoin legal tender in June 2021, hoping it would address some economic issues.
This move faced protests from citizens and the international community, concerned about the country’s lack of internet access. Despite these concerns, the government, led by a young president, moved forward.
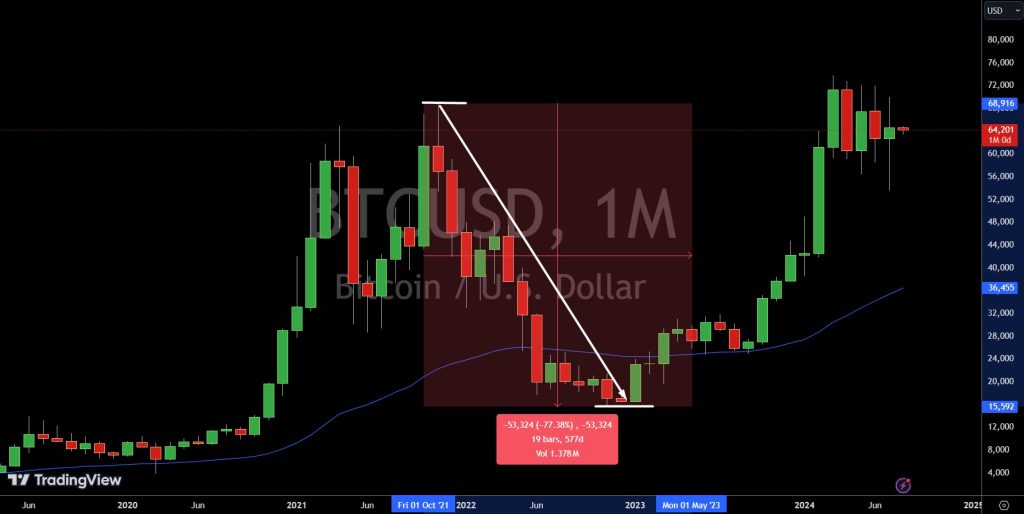
According to a previously published news article:
“Following Bitcoin’s peak in November 2021, its prices fell by 70% as of July 2022, and El Salvador’s Bitcoin reserves have lost about 50% of their value. This is concerning, given the country has $1 billion in debts to pay over the next year.”

- Gold’s Stability: Gold has long backed part of the Swiss Franc and has not experienced the same level of volatility and uncertainty over its long-term value.
- Bitcoin’s Volatility: Bitcoin has experienced declines of 50% or more multiple times, making it a highly volatile asset.
While some praise the government of El Salvador for this experiment, others question Bitcoin’s capability as a safe-haven asset.
The future of Bitcoin as a safe-haven remains uncertain, and it is yet to be seen if it will achieve the stability and acceptance that traditional safe-haven assets like gold have enjoyed.
Bitcoin Investment / Bitcoin Speculation
Bitcoin has been an awesome investment vehicle that has filled many investors’ pockets with handsome gains. The Winklevoss twins, the same who split from Mark Zuckerberg during Facebook’s founding, invested approximately $11m in Bitcoin in 2012 and 2013. This made them billionaires, becoming a $6b fortune.
The buy-and-hold strategy, or ‘hodling’ as it’s otherwise affectionately known by the Bitcoin community, has been a popular Bitcoin strategy that has performed great so far.
Obviously, this depends on when you invested, but generally speaking, it’s the best way for investors to get involved with Bitcoin.
Bitcoin can be traded on forex trading platforms and bitcoin exchanges for speculative or investment purposes. On cryptocurrency exchanges, bitcoin can typically be bought with fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies.
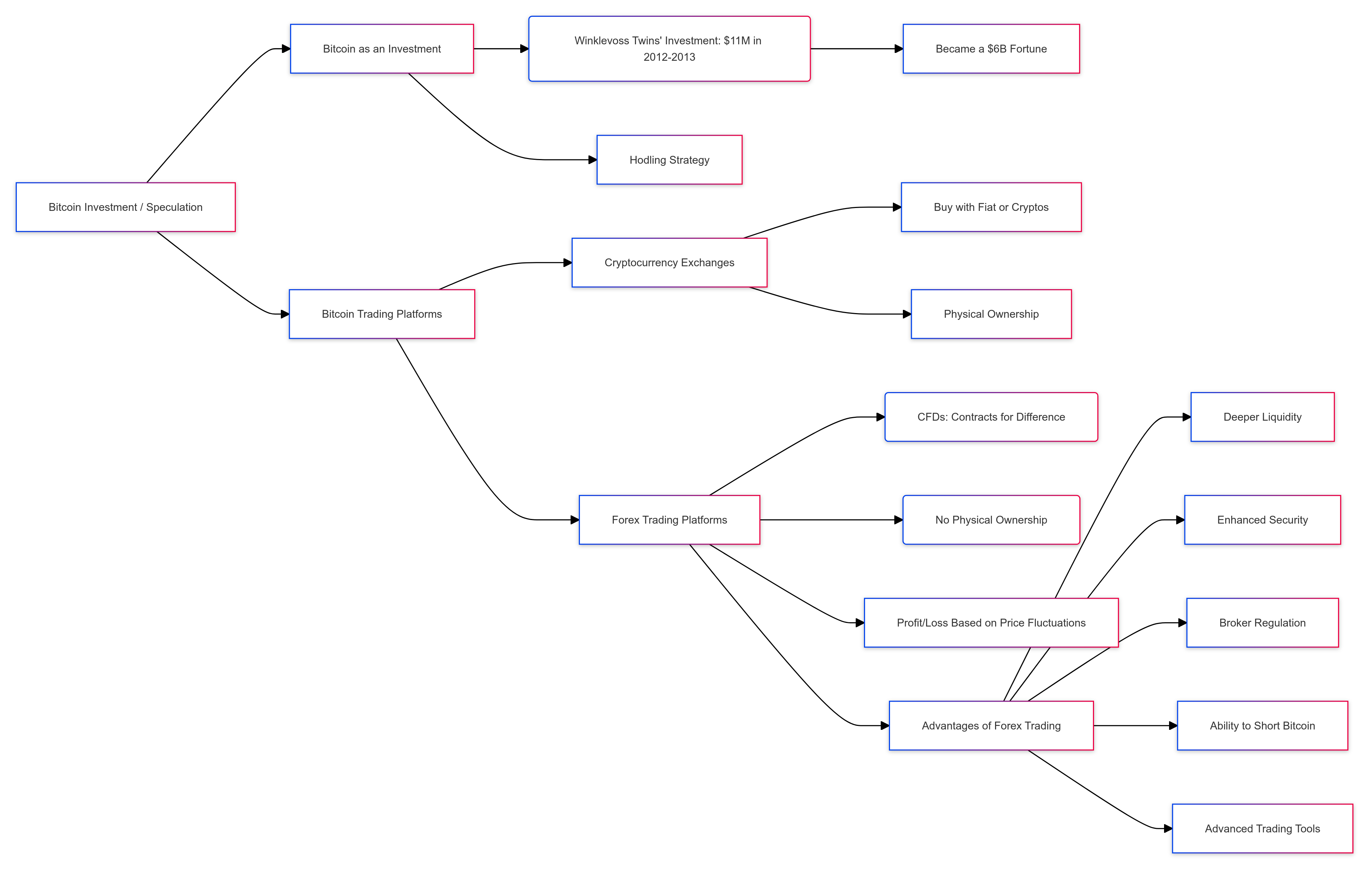
When trading bitcoin on forex trading platforms, traders and investors typically engage in contracts for difference (CFDs) trades and don’t ‘physically’ own bitcoin, unlike exchanges.
Profits or losses are calculated on the fluctuation of the underlying bitcoin price and credited or debited to the traders’ trading accounts.
Trading bitcoin CFDs with forex brokers may have advantages over trading it on bitcoin exchanges.
Some of the advantages include access to deeper liquidity in some instances, security because Bitcoin is not owned (and can therefore not be hacked), proper broker regulation, the ability to short Bitcoin, access to stop loss, take profit, and other orders, and advanced charting and trading tools.
Exploit the cryptocurrency market with price action trading!
Bitcoin can also be traded on social trading platforms like eToro and ZuluTrade with CFDs. On these platforms, investors can copy the trades of cunning traders directly and automatically into their trading accounts.
Follow this link for in-depth information on trading Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies with eToro.
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs, only real crypto assets.

Bitcoin Alternatives
Investors and speculators can trade numerous cryptocurrencies besides Bitcoin.
- Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contract functionality, Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization and continues to be a popular choice among developers and investors.
- Litecoin (LTC): Often referred to as the silver to Bitcoin’s gold, Litecoin offers faster transaction times and a different hashing algorithm.
- Ripple (XRP): Ripple focuses on enabling real-time, cross-border payment systems, making it attractive to financial institutions.
- Cardano (ADA): With a strong emphasis on security and scalability, Cardano aims to create a sustainable and balanced ecosystem for cryptocurrencies.
- Solana (SOL): Known for its high transaction speeds and low costs, Solana is gaining popularity as a scalable blockchain solution.
In addition to cryptocurrencies, traders can easily access other financial markets, including foreign exchange, stocks, bonds, interest rates, commodities, options, and futures, through online trading platforms.
*Learn how to trade ether (Ethereum)
Popular Bitcoin Rumors and Forecasts
Rumours about Bitcoin’s future price movements are always circulating, with predictions varying widely. Bitcoin has experienced numerous sharp pullbacks throughout the years but has continued to trend higher overall.
Forecasts by Influencers:
- Elon Musk: Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk has been a vocal supporter of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. He has hinted at the possibility of Bitcoin reaching new all-time highs, driven by broader acceptance and integration into the financial system.
- Robert Kiyosaki: The author of “Rich Dad Poor Dad” has predicted that Bitcoin could skyrocket to $500,000 by 2025 due to diminishing trust in traditional fiat currencies and increasing adoption of digital assets.
- Cathie Wood: CEO of ARK Invest, Wood has maintained a bullish outlook on Bitcoin, suggesting it could reach $500,000 by 2026 as institutional investors increasingly add Bitcoin to their portfolios.
Only time will tell where Bitcoin’s price will ultimately go, but it remains a focal point of both speculation and investment in the financial world.
Bitcoin in Perspective
One thing about Bitcoin is certain – it has outperformed all ‘traditional’ investment products since it was invented. However, it should be noted that it might not do the same in the next few decades.
Perhaps it will, but how long will money flow into a virtual currency of which the only intrinsic value is its value as a medium of exchange and store of value?
Experienced investors maintain balanced portfolios. Is all of your money in Bitcoin?
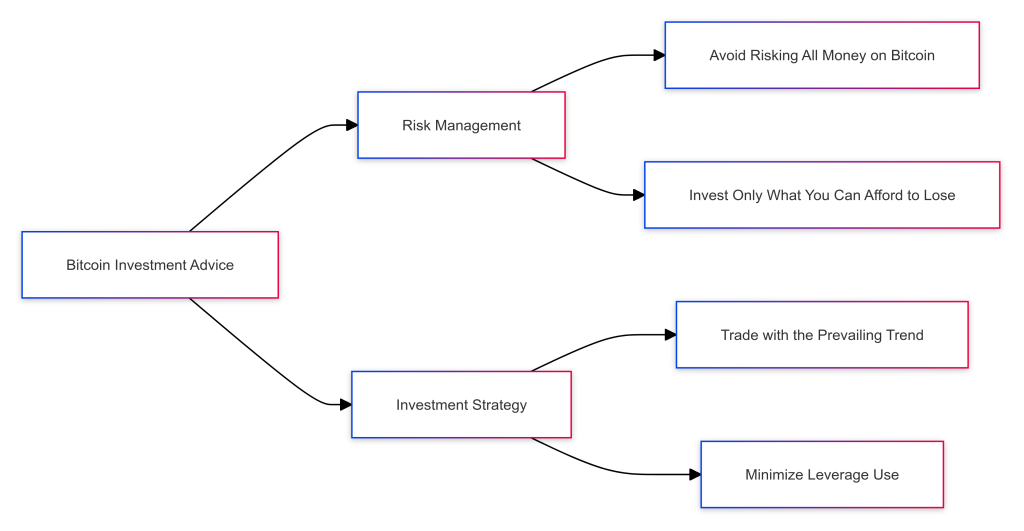
When it comes to trading and investing in Bitcoin, proper risk management should be exercised at all times.
There is potentially a lot of money to be made with Bitcoin trading, but traders should exercise prudence when trading it. The price of bitcoin is very volatile, and risk needs to be managed carefully.
The following investment rules should be applied when trading or investing in Bitcoin, or any cryptocurrency:
- Don’t risk all of your money on bitcoin.
- Only invest or trade with money you can afford to lose.
- Trade with the prevailing trend.
- Don’t use much leverage, if any.
In Conclusion
In terms of intrinsic value and other aspects, bitcoin is completely different from traditional assets like fiat currencies, stocks, and commodities. Nevertheless, bitcoin has outperformed all of these asset classes by far and may continue to do so for quite a while.
Bitcoin’s extreme volatility and persistent trending behaviour make it a grand champion in the trading arena for those who want explosive gains.
Traders who want to engage in the phenomenal Bitcoin market are invited to use FXLeaders’ profitable Bitcoin signals. Those who don’t have access to a reliable Bitcoin broker can choose one from this list of cryptocurrency brokers.