All Types of Forex Orders Explained

Many ordinary people think that the only trade to trade in the financial markets is only by buying and selling. In a certain way that is true – you can only buy and sell, but you can do it in several ways which most brokers accept, as well as in a few other ways, which are not so common.
These types of orders make life easier for traders and they help us perform certain trading strategies. A forex order refers to how you enter and exit the market. As we mentioned above, not all brokers accept all orders, so you will have to check what they allow and what they do not. Below are the types of forex orders explained.
Types of Forex Orders
Market Order
Market orders are the ones where the trade goes in immediately, at the best price available for the execution time. Before, many traders would offer the Actual Price Order, where the trade would open only when the price was at the moment of the execution. Although, in recent years, as the volatility increased, it became increasingly difficult to catch the price exactly where it was at the execution time. So, most forex orders now are Best Available Price Orders, which means that there is a certain degree of slippage when there is volatility, but you can never miss a trade.
Instant Orders
Buy Market Order
A Buy Market Order is pretty straightforward. You basically execute the orders by clicking on the buy button and your broker executes the trade almost instantly, with some slippage if the volatility is high in markets.
Let’s suppose you are buying GBP/USD. The Bid Price is at 1.2052 and the Ask Price is 1.2050.
Assuming that you want to buy the GBP at market price, your forex order would go in instantly and you would have a long position in GBP/USD from 1.2052, if there is no slippage. If there is slippage, then the entry price might be slightly different from that.
Sell Market Order
As with buy market orders, a Sell Market Order is the most basic forex order. You execute the order by clicking on the sell button and your broker executes the trade almost instantly, slippage or not.
Let’s take the same example with GBP/USD, with the same Bid Price and Ask Price. If you want to execute a sell market order on this pair, then you would have a short position in this pair, with an entry price of 1.2050. Again, the entry price also depends on the volatility and slippage.
Stop Loss
As in all forex trades, you would be better off if you used the option of Stop Loss to protect your trade. If you are buying at 1.2052, then it would be wise to put the stop loss at 1.1990, below the big round level at 1.20 which should offer support, in order to give the trade some room to breathe.
In the option of a market order, traders have to place the stop loss after the trade is opened, click on the edit button of the trade and then enter/edit stop loss.
Take Profit
Some traders like to keep the take profits open when they trade forex and that’s a fine idea if you are following markets closely. But, we advise that you place a Take Profit Target so your profits don’t evaporate if the market turns against you after some time.
As with the stop loss, when you open a buy market order you have to place the take profit target after you open the trade, by right-clicking on the trade, edit button and then place the desired take profit target, after careful analysis.
Trailing Stop Loss
A trailing stop-loss order is not a static target, but rather a moving stop order attached to a forex trade, which follows the market price. A normal stop-loss order attached to trade is a static level where you would normally throw in the towel, giving up on the trade and taking a loss. While the trailing stop follows the price by a number of pips.
If you are buying the GBP/USD at 1.2052 and you place a 50 pips trailing stop, then your stop-loss is immediately at 1.2002. If the price moves down against you, then your trade will close at 1.2002.
If the price moves 50 pips higher at 1.2102, then the stop loss of the trade will be at 1.2052, which means it will be at breakeven. If GBP/USD declines, then the trade will stop 50 pips below the highest price, at 1.2052. If the price moves higher to 1.2200, then the stop loss will shift higher to 1.2150. So, a trailing stop follows the price at 50 pips below the highest level reached, or whatever amount you may find reasonable to place.
A trailing stop loss for a sell position is the opposite of buying. You place the stop 50 pips above the current market price and it will follow the price as it falls down. If the price falls to 1.19, then the trailing stop will be at 1.1950.
Stop Orders
A Stop Order is an order that is not executed immediately, or might not even be executed at all for that matter, if the price doesn’t reach the entry price you placed. When placing a buy or stop order, you do that with an intention to enter the trade at a different price than the current one. With stop orders you either Sell Below the Market Price or Buy Above the Market Price.
Pending Orders
Buy Stop Orders
The intention of a buy stop order is to enter a trade on the long side above the current market price. That seems a bit odd because you would want to get the best/lowest possible entry price for a buy position. But, that works in cases when you expect a possible breakout.
If a forex pair is trading in a range or in a triangle, or below a resistance area and you think that there are good chances that a break might happen to the upside, then you place a Buy Stop Order above the resistance. In the case of GBP/USD, if this pair is trading at 1.2050 and the resistance area is below 1.21, then you might place a buy stop order at 1.2110, because we know that resistances often turn into support.

A buy stop order to buy GBP/USD in case of a breakout above the resistance
Sell Stop Orders
The Sell Stop Order is basically the opposite. Again, you would want the best/highest entry price for a sell position, but if the support is not broken as planned, you don’t want to be caught on the wrong side when the pair bounces higher. That’s the reason for the sell stop orders, and the opposite for the buy stop orders.
In the case of GBP/USD again, supposing that there is a support area around 1.20, which is a big round level, it would be wise to place a sell stop order at 1.1990. The break of a major support area is often followed by a crash, or at least a continuation of the downside momentum, since a lot of stop losses get triggered. A good stop loss would be at 1.2030s, targeting 1.19 at least with the take profit target.
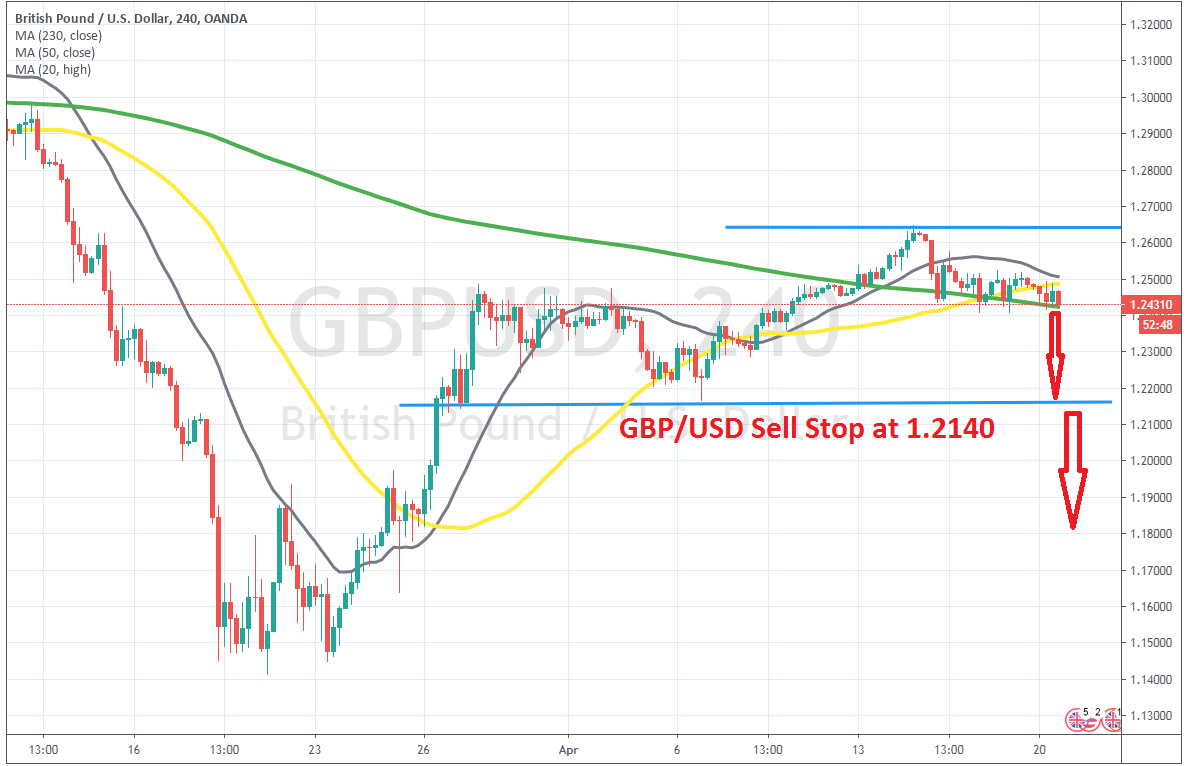
Sell stop order to sell GBP/USD below support in case of a breakout to the downside
Limit Orders
Limit Orders are the opposite of stop orders. It is not executed instantly and might not even get executed if the price doesn’t reach the entry price you placed for the trade. But, it has better chances to be executed and makes more sense than the stop orders. With stop order, you either Sell Above the Market Price or Buy Below the Market Price.
Buy Limit Orders
When placing a Buy Limit Order, your intention is to buy a forex pair at a lower price than the current market price. This sort of trade works best when a forex pair is trading inside a range and you expect the price to fall to the lower bound of the range or the support area and bounce from there.
In case of the GBP/USD, when this pair is trading at 1.2050 and you think that the decline might continue until 1.2000, where there is a big support area. You place a buy limit order at 1.2010, hopping that this pair will fall until there and will then bounce higher. With the Buy Limit Trade, you get the Lowest Entry Price.

A buy limit order to go long on GBP/USD above the support
Sell Limit Orders
The Sell Limit Order is the opposite of the buy limit orders. You expect that the price of a forex pair will increase until a certain level, where it will then start to weaken and eventually reverse back down. The limit orders make much more sense than the stop orders since you get the Highest Entry Price for a Sell Limit Order.
If there is a resistance area surrounding 1.21 in GBP/USD and the price is going up, then you would better want to wait when the actual market price is at 1.2050. So, you place a sell limit order at 1.2090, with a stop above 1.21 and take profit at 1.2010, above the support.

A sell limit order to sell GBP/USD below the resistance in case it holds
Other Forex Orders
These forex orders are not that usual. Most forex brokers usually only accept/offer you to trade markets through the normal orders like instant execution buy/sell orders, stop orders, limit orders, while some others also accept some weird orders. You have to check with your broker if they accept such orders.
Good For the Day Orders
Good for the Day (GFD) orders are not so uncommon, to be honest. As the name implies, these kinds of orders last until markets close. When you open such trades in stock markets, they remain active until the stock exchange of that country closes. For example, if you are trading in the London Stock Exchange, say buying FTSE100, then that kind of trade would remain open until 5 pm GMT, when the LSE closes. If buying shares in the New York Stock Exchange, then that trade would remain open until 11 GMT, when the NYSE closes. The same closing time goes for forex trades as well, they last until 11 pm GMT when North American markets close.
There are also Pending GFD Orders. These orders remain pending until markets close. If they are triggered, they continue until the take profit or stop loss targets are reached, otherwise if they don’t get triggered during that day, they are canceled.
Good Till Cancelled
A Good Till Cancelled (GTC) order, as the name, implies stays on until you manually close it. These types of orders mainly refer to pending orders, which you place to buy/sell at a different price than the actual one. If the price reaches the entry-level, then the trade goes on, if not, then it is canceled.
GBP/USD is trading at the same level as in the above example at 1.2050 and you place a sell order at 1.21 with a stop at 1.2130 and take profit at 1.2010, lasting only for the day. If the Ask Price reaches 1.21, the trade is triggered, if the price doesn’t reach 1.21 until 5 pm GMT time, then the trade is canceled.