Experts Predict High Demand for New Savings Bond As Investors Seek Safe and Reliable Options in Uncertain Economic Times
All savings bonds feature the same interest rate. Thus, they are all predictable and usually generate higher revenues than stocks. The best savings bonds respond quickly to market fluctuations. In simple terms, saving bond yields are likely to fall with the falling interest rates thus, raising prices. One factor contributing to the high demand for savings bonds is the current credit risk in the economy. But what are the benefits of investing in savings bonds?
Benefits of Savings Bond
Generally, savings bonds tend to be less risky and volatile than stocks. Whenever an investor holds bonds to maturity, they offer consistent and stable returns. Saving rates at the bank or money market accounts are often lower than interest rates on saving bonds. According to the 1961 Income Tax Act, taxpayers can leverage up to 20,000/- tax deductions if they invest in government-backed bonds.
Meanwhile, saving bonds can benefit from a surge in inflation rate as they cover inflation-adjusted and fixed-rate returns. The variable rate changes with the monthly Consumer Price Index while the US Treasury Department sets the fixed rate. Therefore, saving bonds can maneuver between these rate returns to protect your money from inflation. Bonds can also be a means of earning a predictable return and preserving capital.
Factors Contributing To High Demand For Savings Bond
In any case, bond investments offer a reliable income stream from interest payments before maturity. But saving bonds that take longer to mature are extra sensitive to interest rate changes and face the impacts of inflation. In simple terms, the inflation rate affects the actual rate of fixed-income investments.
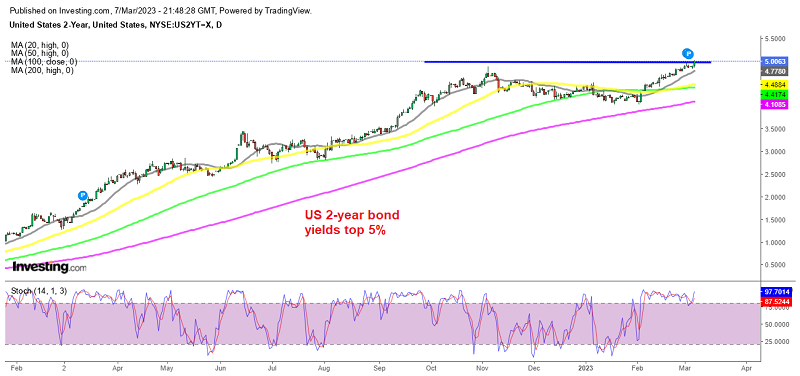
Thus, the fluctuation in real return might deter away investors, resulting in lower bond prices. Financial experts have anticipated a negative overall bond growth throughout the first half of 2023. For instance, they project that the S&P 500 earnings might drop by up to 5.7% in the first quarter and 3.7% in the second quarter.
Potential Risks And Drawbacks
The rising interest rates pose the worst risk for bond investors. Rising interest rates can lead to lower bond prices, which reflect the investors’ ability to record a higher interest on their investment elsewhere. For the most part, lower saving bond prices reflect higher returns or yields on the bonds. The current record-high inflation rate lowers the buying power of bond future principal and coupons.
While bonds do not offer extraordinarily higher returns, they are more vulnerable to inflation rate fluctuations. When inflation results in higher interest rates in the economy, it negatively impacts bond prices. However, inflation-linked bonds come with a structure that protects investors from inflation risks. Overall, the principal (or nominal) and the coupon stream rise concurrently with the inflation rate to protect investors from its negative impact.
Types Of Savings Bonds
Generally, savings bonds fall into two main categories; those with fixed rates and those that are inflation-indexed. Interestingly, some inflation-indexed savings bonds bear fixed rates plus a second rate that is based on inflation. For instance, in the US, the government issues two types of savings bonds. These include Series EE bonds that bear a fixed rate and Series I bonds that are constantly adjusted for inflation.
As mentioned earlier, interest rates will impact bond prices either positively or negatively. Thus, for the Series EE fixed rate bonds, investors are assured to see their investment double after 20 years of investing in them. Interestingly, if that doesn’t happen automatically, the government will adjust them to guarantee the desired outcome. Also, these bonds will continue to accrue interest rates for 30 years from the day they are issued.
On the other hand, Series I bonds boast two rates; the first is fixed and remains the same for the entirety of the investment. While the other is adjusted for inflation every six months. Like Series EE bonds, these bonds accrue interest for 30 years after being issued.
Conclusion
In uncertain economic times, investors are increasingly turning to safe and reliable options such as savings bonds. With their predictable interest rates and less volatility compared to stocks, savings bonds offer consistent and stable returns. They can also protect against inflation and provide tax benefits. However, investors should be aware of the potential risks and drawbacks, such as the impact of rising interest rates on bond prices. Overall, savings bonds are a valuable investment option for those seeking a secure and steady income stream.