Trading Course
Risk and Money Management
- Risk and Money Management
- 10 BEST FOREX BROKERS
- Market Volatility
- Stop Loss Settings – How, Where, When
- How to set your Stop Loss
- The Risks of Leverage
- Trading Plan and Trading Journal
- Trading Checklist
- How to Choose the Right Broker, Platform, and Trading System
- 10 BEST FOREX BROKERS
- Practice
Risk and Money Management
Risk and Money Management, we will discuss how to maximize your profits while minimizing your risk using one of the most important tools of forex trading – proper money and risk management. This will help you mitigate your risk and still allow you to make a nice profit.
- ☑️ Market Volatility
- ☑️ Stop Loss Settings: How, Where, When
- ☑️ The Risks of Leverage
- ☑️ Trading Plan + Trading Journal
- ☑️ Trading Checklist
- ☑️ How to Choose the Right Broker – Platforms and Trading Systems
and much, MUCH more!
10 BEST FOREX BROKERS
 | MIN DEPOSIT $100 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $50 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $25 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $200 | SIGN-UP BONUS No | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $4 | SIGN-UP BONUS No | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $5 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $0 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $20 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $10 | SIGN-UP BONUS No | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $1 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
Risk management is a crucial part of any trading plan. It helps you stay in the game longer, even through losses or bad luck. Think of Forex as a market, not a casino — reckless trading leads to failure.
Only risk a small portion of your capital per trade. Don’t go all-in on a single position. Diversifying helps reduce risk. Even with a solid plan that wins 70% of the time, you must prepare for losing streaks by keeping reserves.
Great traders don’t just avoid losses — they cut losses small and let profits run. Risk levels also depend on factors like the currency pair, trading day (e.g., volatile Fridays), time of year, and major news events.
Focus on these three essentials: smart position sizing, timing, and staying informed. Most trading platforms let you manage and update risk settings in real time.
Can you guess what they are?
- Leverage
- Setting a “Stop Loss“
- Setting a “Take Profit“
Another good option is called “Trailing Stops”: setting trailing stops allows you to retain your earnings while the trend goes in the right direction. For instance, say you set a Stop Loss 100 pips higher than the current price. If the price reaches this point and continues to go up, nothing will happen. But if the price starts dropping, reaching this point again on its way down, the position will automatically close, and you will exit the trade with 100 pips of revenue. That is how you can avoid future decreases that will eliminate your profits to date. You will be satisfied with your profits up to that point.

Market Volatility
The volatility of a given pair determines how risky it is to trade it. The stronger the market volatility, the riskier it is to trade with this pair. On the one hand, strong volatility creates great earning options due to the many powerful trends. On the other hand, it might cause quick, painful losses. Volatility is derived from fundamental events that influence the market. The less stable and solid the economy is, the more volatile the charts will be.
If we look at the major currencies for example: The most secure and stable majors are USD, CHF, and JPY. The reason for this is that these 3 majors are used as reserve currencies The central banks of most developed economies hold these currencies, with an inevitable, major impact on both the global economy and exchange rates. USD, JPY, and CHF constitute the majority of the global currency reserves, which are enormous.
EUR and GBP are also powerful, but during recent years they have been considered to be less stable – their volatility is higher. Particularly, the GBP after the Brexit referendum. The Euro lost about five cents after the referendum, while the GBP lost more than 20 cents and the trading range in GBP pairs remains several hundred pips wide.
How to determine the level of volatility of a certain forex pair:
- Moving Average: Helps the trader to follow the ups and downs of a pair during any period, by examining the pair’s history.
- Bollinger Bands: When the channel becomes wider, volatility is high. This tool evaluates the current status of the pair.
- ATR: This tool collects averages throughout chosen periods. The higher the ATR, the stronger the volatility, and vice versa. ATR represents historical evaluation.

Stop Loss Settings – How, Where, When
We have emphasized this numerous times throughout the course. There isn’t even one person in the world, not even Mr. Warren Buffett himself, who can predict all price movements. No trader, brokerage, or bank can foresee every trend at any given time. Sometimes, Forex is unexpected and may cause us losses if we are not careful. No one could predict the social revolutions that occurred in the Arab markets at the beginning of 2011, or the major earthquake in Japan, yet fundamental events like these have left their marks on the global Forex market!
Stop Loss is a highly important technique, designed for reducing our losses in times when the market behaves the opposite way to our trades. Stop Loss plays a critical role in every successful trading plan. Think about it- Sooner or later you will make mistakes that will lead to losses. The idea is to reduce losses as much as you can while expanding your earnings. A Stop Loss order allows us to survive bad, losing days.
Stop Loss exists in every online trading platform. It is executed when we give the order. It appears right next to the price quotation and call for action (Buy/Sell).
How to set a stop-loss order? Place a stop-loss sell order on long positions just below the support level, and a stop-loss buy order on short positions just above the resistance.
For example: if you want to go long on EUR at USD 1.1024, a recommended stop order should be a little lower than the current price, say around USD 1.0985.

How to set your Stop Loss
Equity Stop: Determined how much we are willing to risk out of our total amount, in percentage terms. Assume you have $1,000 in your account when deciding to enter a trade. After thinking for a few seconds, you decide that you are willing to lose 3% of your total USD 1,000. It means that you can afford to lose up to USD 30. You will set the Stop Loss below your buying price, in a way that will permit a maximum, potential loss of USD 30.
That way you will be left with USD 970 in the event of a loss. At this point, the broker will automatically sell your pair and remove you from the trade. More aggressive traders set stop-loss orders around 5% distant from their purchase price. Solid traders are usually willing to risk around 1%-2% of their capital.
The main problem with equity stop is that while it takes into consideration the trader’s financial condition, it doesn’t take into consideration at all current market conditions. A trader is examining himself instead of examining trends and signals produced by the indicators he uses.
In our opinion, it is the least skillful method! We believe that traders have to set a Stop Loss according to market conditions and not on how much they are willing to risk.
Example: Let’s assume that you have opened a USD 500 account, and you want to trade a USD 10,000 lot (standard lot) with your money. You wish to put 4% of your capital at risk (USD 20). Each pip is worth USD 1 (we have already taught you that in standard lots, each pip is worth 1 currency unit). According to the equity method, you would set your stop loss 20 pips away from the resistance level (you plan to enter the trend when the price reaches the resistance level). You choose to trade the pair EUR/JPY.
It is very important to know that when trading the majors, as in our example, a 20 pips move might last just a few seconds, very brief! It means that even if you are right with your overall predictions on a future trend’s direction, you might not get to enjoy it because just before the price went up it slipped back and touched your Stop Loss. That´s why you must place your stop at reasonable levels. If you can’t afford it because your account is not big enough, then you must use some money management techniques and probably reduce the leverage.
Let’s see what a stop loss looks like on the chart:
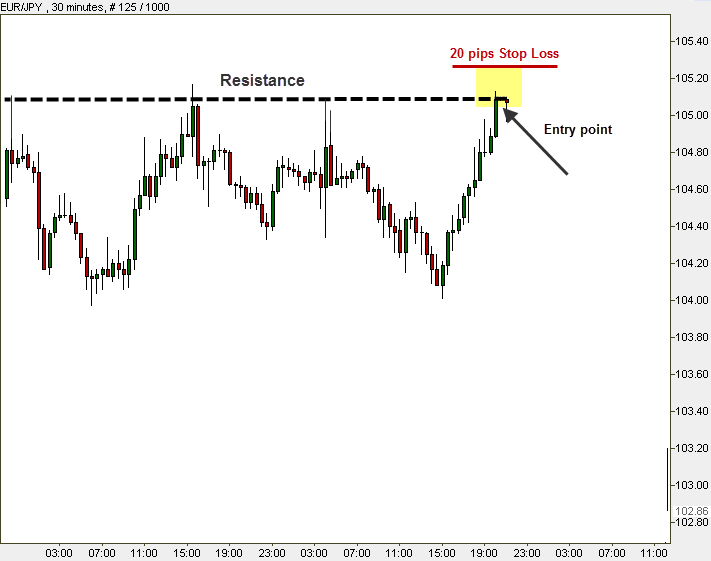
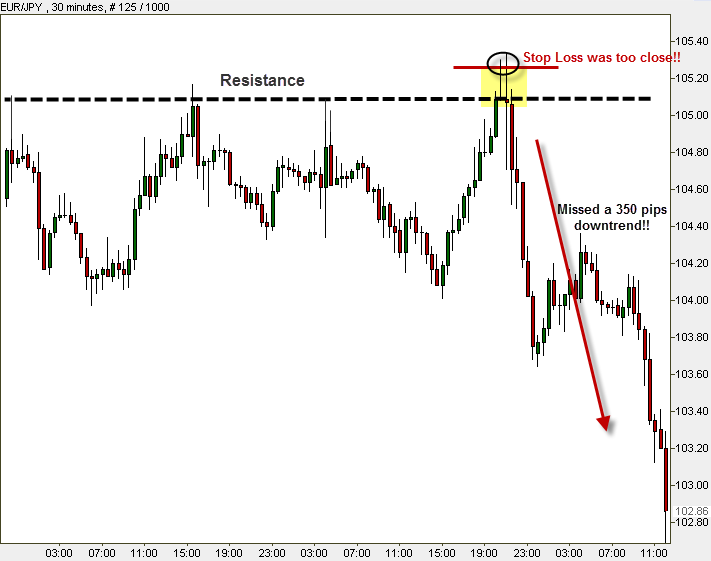
Chart Stop: Setting a Stop Loss not based on price, but according to a graphical point on the chart, around support and resistance levels for instance. Chart Stop is an effective and logical method. It gives us a safety net for an expected trend that has not taken place yet. Chart Stop can be either determined by you in advance (Fibonacci levels are recommended areas for setting a Stop Loss), or under a specific condition (you can decide that if the price reaches a crossover point or a breakout, you close the position).
We recommend working with Chart Stop Losses.
For example: if you plan to enter a BUY order when the price reaches the 38.2% level, you would set your Stop Loss between levels 38.2% and 50%. Another option would be to set your Stop Loss just below the 50% level. By doing so you would give your position a bigger chance, but this is considered to be a slightly more dangerous decision that might cause more losses if you are wrong!
Volatility Stop: This technique was created to prevent us from exiting trades due to temporary volatile trends that are caused by current pressure among the traders. It is recommended for long-term trading. It is based on the claim that price moves according to a typically clear and routine pattern as long as there is no major fundamental news. It works on expectations that a certain pair is supposed to move during a period within a given pips range.
For example: if you know that EUR/GBP has moved throughout the past month an average of 100 pips a day, you would not set your Stop Loss 20 pips from the opening price of the current trend. That would be inefficient. You would probably lose your position not because of an unexpected trend, but because of the standard volatility of this market.
Tip: Bollinger Bands are an excellent tool for this Stop Loss method, setting Stop Loss outside of the bands.
Time Stop: Setting a point according to a time frame. It is effective when the session has already been stuck for a long period (price is very stable).
The 5 Don’ts:
- Don’t set your Stop Loss too tight to the current price. You don’t want to “strangle” the currency. You want it to be able to move.
- Don’t set your Stop Loss according to position sizing, meaning according to the amount of money that you wish to put at risk. Think of a poker game: it is the same as deciding upfront that you are willing to put on the next round up to USD 100 maximum, out of your USD 500. It would be silly if a pair of Aces appears…
- Don’t set your Stop Loss exactly on the support and resistance levels. That’s a mistake! In order to improve your chances you need to give it a little space, as we have already shown you countless cases where the price broke these levels by just a few pips, or for a short time, but then moved right back.
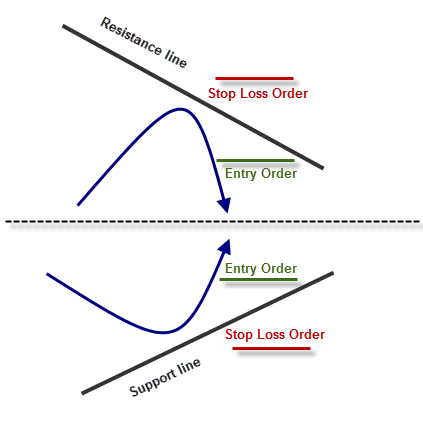
Remember- levels represent areas, not specific points!
- Don’t set your Stop Loss too far from the current price. It may cost you a lot of money just because you have not paid attention or have looked for an unnecessary adventure.
- Don’t change your decisions after making them!! Stick to your plan! The only case in which it is advised to reset your Stop Loss is in case you are winning! If your position makes profits, you had better move your Stop Loss towards your profitable zone.
Don’t expand your losses. By doing so you let your emotions take over your trading, and emotions are the biggest enemies of experienced pros! It is just like entering a poker game with a budget of USD 500 and buying USD 500 more with chips after losing the first USD 500. You can guess how it might end – big losses

The Risks of Leverage
You have already learned about the significance of leverage and the possibilities it offers. With leverage, you can multiply your profits and earn much more than your real money could have earned. But in this part we will talk about the consequences of Over Leverage. You will understand why irresponsible leverage might be devastating for your capital. The number one reason for traders’ commercial demise is high leverage!
Important: Relatively low leverage can create tremendous profits for us!
Leverage – Controlling a large amount of money while using a small part of it out of your own money, and “borrowing” the rest from your broker.
| 🅰️ Required Margin | 🅱️ Actual Leverage |
| 5% | 1:20 |
| 3% | 1:33 |
| 2% | 1:50 |
| 1% | 1:100 |
| 0.5% | 1:200 |
Remember: We recommend you not to work with leverage of more than x25 (1:25) under any conditions! For example, you should not open a standard account (USD 100,000) with USD 2,000, or a mini account (USD 10,000) with USD 150! 1:1 to 1:5 are good leverage ratios for large hedge funds, but for retail traders, the best ratio varies between 1:5 and 1:10.
Even very experienced traders who consider themselves big risk lovers do not use leverage of more than x25, so why should you? Let’s study the market first, earn some real money and get some experience, working with low leverage, then, move to slightly higher leverage.
Some of the commodities can be very volatile. Gold, Platinum, or Oil move hundreds of pips in a minute. So, if you want to trade them your leverage must be as close to 1 as possible. You should not turn trading into a gamble.
Example: This is what your account would look like when you open a USD 10,000 account:
| 📈 Balance | 📉 Equity | 📊 Used Margin | 💹 Available Margin |
| USD 10,000 | USD 10,000 | USD 0 | USD 10,000 |
Let’s assume that you open a position with USD 100 initially:
| 📈 Balance | 📉 Equity | 📊 Used Margin | 💹 Available Margin |
| USD 10,000 | USD 10,000 | USD 100 | USD 9,900 |
Assume that you decide to open 79 more lots on this pair, meaning a total of USD 8,000 will be in use:
| 📈 Balance | 📉 Equity | 📊 Used Margin | 💹 Available Margin |
| USD 10,000 | USD 10,000 | USD 8,000 | USD 2,000 |
Right now, your position is very risky! You are dependent on the EUR/USD. If this pair goes bullish you win a great deal of money, but if it goes bearish you are in trouble! Your equity will decrease as long as EUR/USD loses value. The minute the equity falls under your used margin (in our case USD 8,000) you will receive a “margin call” on all of your lots.
Say you bought all 80 lots at the same time and same price:
25 pips decrease will activate a margin call. 10,000 – 8,000 = USD 2,000 loss because of 25 pips!!! It can happen in seconds!!
Why 25 pips? In a mini account, each pip is worth USD 1! 25 pips scattered over 80 lots are 80 x 25 = USD 2,000! At that exact moment, you have lost USD 2,000 and are left with USD 8,000. Your broker will take the spread between the initial account and your used margin.
| 📈 Balance | 📉 Equity | 📊 Used Margin | 💹 Available Margin |
| USD 8'000 | USD 8'000 | 0 USD | 0 USD |
We still have not mentioned the spread that the brokers take! If in our example the spread on the pair EUR/USD is fixed at 3 pips, the pair needs to decrease only 22 pips for you to lose USD 2,000!
Important: Now you understand even better why it is so important to set a Stop Loss for every position you open!!
Remember: In a mini account, each pip is worth USD 1 and in a standard account, each pip is worth USD 10
| 📈 Change in your account (In %) | 📉 Margin required | 📊 Leverage |
| 100% | USD 1,000 | 100 : 1 |
| 50% | USD 2,000 | 50 : 1 |
| 20% | USD 5,000 | 20 : 1 |
| 10% | USD 10,000 | 10 : 1 |
| 5% | USD 20,000 | 5 : 1 |
| 3% | USD 33,000 | 3 : 1 |
| 1% | USD 100,000 | 1 : 1 |
If buying a pair with a standard lot (USD 100,000) and its value goes down 1%, this is what would happen with different leverages:
High leverages, such as x50 or x100 for instance, could produce astronomical gains, of tens and hundreds of thousands of dollars, in a very short time! But you should only consider this if you are prepared to take serious risks. A trader can use these high ratios only in extreme conditions when the volatility is low and the price direction is almost 100% confirmed, probably around the time the US session closes.
You can scalp a few pips with high leverage because the volatility is minimal and the price trades in a range, which makes the direction easily detectable in the short term.
Remember: The ideal combination is low leverage and large capital on our accounts.

Trading Plan and Trading Journal
Just as a good business plan is required when starting a new business, to trade successfully we want to plan and document our trades. Once you have decided on a trading plan, be disciplined. Don’t get tempted to stray from the original plan. The plan that a given trader uses, tells us a great deal about his character, expectations, risk management, and trading platform. A plan’s core is how and when to exit trades. Emotional action can cause damage.
Determining your goals is important. For example how many pips or how much money do you plan to earn? Which point on the chart (value) do you expect the pair to reach?
For example: it would not be clever to set a short-term trade if you have not got enough time during the day to sit in front of your screen.
Your plan is your compass, your satellite navigation system. 90% of online traders do not build a plan, and that, among other reasons, is why they do not succeed! Trading Forex is a marathon, not a sprint!
Remember: After putting your energy into the MARKET LEADERS FOREX COURSE you are ready to implement, but do not be smug! Let’s try to get into it gradually. Whether you wish to open a USD 10,000 or USD 50,000 account, we recommend you to hold your horses. It is not advisable to invest all your capital in a single account or to take unnecessary risks.
Your trading plan has to include several items:
What is hot in the Forex market and other markets, such as commodities and indices markets? Be tuned to the Financial markets forums and communities. Read what others write, follow current hot trends in the market, and be aware of less fashionable opinions. Make FXLeaders.com your Forex opportunities window.
Follow the economic news, as well as general global news. You have already become aware that these have a tremendous impact on currencies.
Try to follow daily global commodity prices (gold or oil for example). They often have a large influence on some currencies, such as the USD for example, and vice versa.
Follow forex signals, which at the very least give you an experienced opinion of what traders and analysts think of a forex pair at a certain time.
A trading journal is good for documenting your actions, thoughts, and comments. We do not mean “Dear diary, I woke up this morning and felt marvelous!” You will see that in the long run, you will be able to learn a lot from it! For example- which indicators worked fine for you, what events to keep a distance from, market diagnoses, your favorite currencies, statistics, where have you gone wrong, and more…
An effective journal includes several points:
- The strategy behind each of your executions (How and why did you act that particular way?)
- How did the market respond?
- A sum of your feelings, doubts, and conclusions

Trading Checklist
To get things straight, we conclude the critical stages with a correct trading strategy:
- Deciding on a timeframe – What timeframes do you wish to work on? For example, daily charts are advised for fundamental analysis
- Deciding on the right indicators for identifying trends. For example, choosing 2 SMA lines (simple moving averages): one would be 5 SMA and the other would be 10 SMA, and then, waiting for them to intersect! Combining this indicator with Fibonacci or Bollinger Bands can be even better.
- Using indicators that confirm the trend – RSI, Stochastic, or MACD.
- Deciding on how much money we are willing to risk losing. Setting Stop Losses is essential!
- Planning our entries and exits.
- Setting a list of iron rules for our position.

How to Choose the Right Broker, Platform, and Trading System
You don’t need to use your phones, go to your bank, or employ an investment consultant with a diploma to trade the Forex market. All you need to do is choose the right forex broker and the best trading platform for you and simply open an account.
Types of brokers:
The following table explains the 2 main groups of brokers:
| 📈 Dealing Desk (DD) | 📉 Dealing Desk (DD) |
| No Dealing Desk (NDD) | No Dealing Desk (NDD) |
| Spreads are fixed | Variable spreads |
| Trade against you (takes the opposite position to yours). Market makers | Operate as bridges between traders (customers) and liquidity providers (banks) |
| Quotes are not precise. There are re-quotes. Can manipulate prices | Real time quotes. Prices come from market providers |
| Broker controls your trades | Automatic executions |
NDD brokers guarantee an unbiased trade, 100% automatic, without the intervention of dealers. Therefore, there cannot be a conflict of interest (it might happen with DD brokers, who serve as your banks and at the same time trade against you).
There are several important criteria for choosing your broker:
Security: We advise you to choose a broker who is subject to regulation by one of the major regulators – such as the American, German, Australian, British, or French regulators. A brokerage that works without regulatory supervision at all might be suspicious.
Trading Platform: The platform has to be very user-friendly and clear. It also has to be simple to operate, and include all technical indicators and tools that you wish to use. Extras such as news sections or commentaries add to the quality of the broker.
Transaction Costs: You have to check and compare spreads, fees, or other commissions if there are any.
Call to action: Accurate price quotes and fast reactions to your orders.
An optional practice account: Once again, we do recommend practicing a little on your chosen platform before opening a real account.
Three simple, quick steps to start trading:
- Choosing an account type: Determines the capital that you wish to deposit, which derives from the amount of money that you wish to trade with.
- Registration: Includes filling up your details and signing up.
- Account Activation: At the end of the process you get an email from your broker, with a username, password, and instructions.
Tip: Most of our most recommended brokers, such as eToro and AvaTrade, offer a personal account manager when depositing $500 or more in your account. A personal account manager is a fantastic and important service, which you want on your side. It might be the difference between struggling and succeeding, especially if you are a beginner. An account manager will help you with every technical question, tip, trading advice, and more.
Remember: Ask for a personal account manager when opening an account, even if it means calling the brokerage’s help desk.
We strongly recommend opening your account with the big, reliable, and popular brokers from the FXMarketLeaders recommended forex brokers. They have already earned a high reputation and a large, loyal clientele.
10 BEST FOREX BROKERS
 | MIN DEPOSIT $100 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $50 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $25 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $200 | SIGN-UP BONUS No | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $4 | SIGN-UP BONUS No | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $5 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $0 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $20 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $10 | SIGN-UP BONUS No | Visit Now |
 | MIN DEPOSIT $1 | SIGN-UP BONUS Yes | Visit Now |
Practice
Go to your practice account. Once the trading platform is in front of you. Let’s do a little general review of what you have just learned:
Start to wander a little between different pairs and timeframes on the platform. Observe and spot different levels of volatility, low to high. Use indicators like Bollinger Bands, ATR, and Moving Averages to help you with volatility tracking.
Practice Stop Loss orders on each of your positions. Get used to working with several levels of Stop Loss and Take Profit settings, based on your strategic management
Experience different levels of leverage, Start writing a journal and, memorize the MARKET LEADERS FOREX COURSE Trading Checklist.
Revision Questions
- When buying a single Standard Dollars Lot, with 10% margin, what is our actual deposit?
- We have deposited USD 500 in our account and we wish to trade with x10 leverage. How much capital will we be able to trade with? Say we buy EUR with this total amount, and EUR rises five cents. How much money would we make?
- Stop Loss: What is the difference between an Equity Stop and a Chart Stop? Which method is better?
- Would it be right to set a Stop Loss on the support/ resistance level? Why?
- Is it advised to leverage? If yes, to what level?
- What are the main criteria for a good broker?
Answers
- USD 10,000
- USD 5,000. $250
- Chart Stop, because it relates not only to economic conditions but to market trends and movements as well.
- No. Keep a little distance. Leave a bit of space. Support and resistance levels represent areas and we don’t want to miss great trends due to a minor exception of a couple of candlesticks or their shadows
- It could be a good idea, but not under all circumstances. It depends on how high the risks you are willing to take. Heavy traders who trade with large capital on long-term trades do not necessarily leverage. Leverage certainly can bring great profits, but it is not advised to exceed the x10 level.
- Security; Reliable customer service; Trading platform; Transaction cost; Accurate price quotes and speedy reactions to your orders, social trading, and a friendly platform for automatic trading.
In Chapter 11 – Forex in Relation to Stocks and Commodities and Trading with MetaTrader you will learn about the relationship between commodities and indices to the forex market. In addition, you will learn how to use MetaTrader, the most common trading platform today.
